There are many interrelated factors that affect productivity. For example, production can vary on a daily basis due to many lots of small quantities or great fluctuations in quantities, or pressures for short lead times or fluctuation in manpower. It can be a very daunting task to analyze data on all these variables, so it is important to keep things simple and visible so that results can be accomplished.
Simple example to
improve productivity
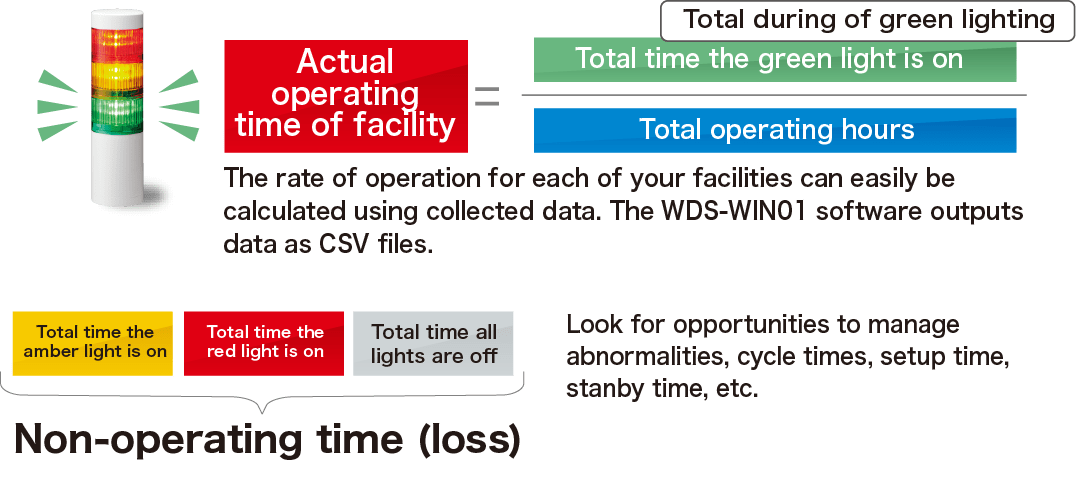
The objective is to improve equipment productivity. Simply bring to light how much operation and non-operation time there is.

Simple example to
improve productivity

Simple data can give an unbiased, thorough overview of the entire system, helping to identify areas for improvement on-site. Initially, the implementation area will be small, so the results will be quick.
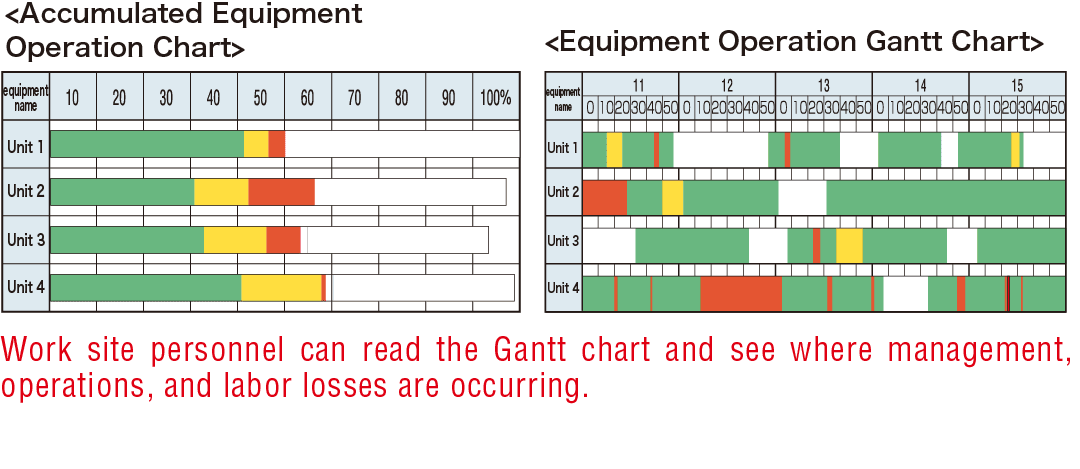
Quantify operational outcomes to evaluate the effectiveness of the improvement methods.
Tip
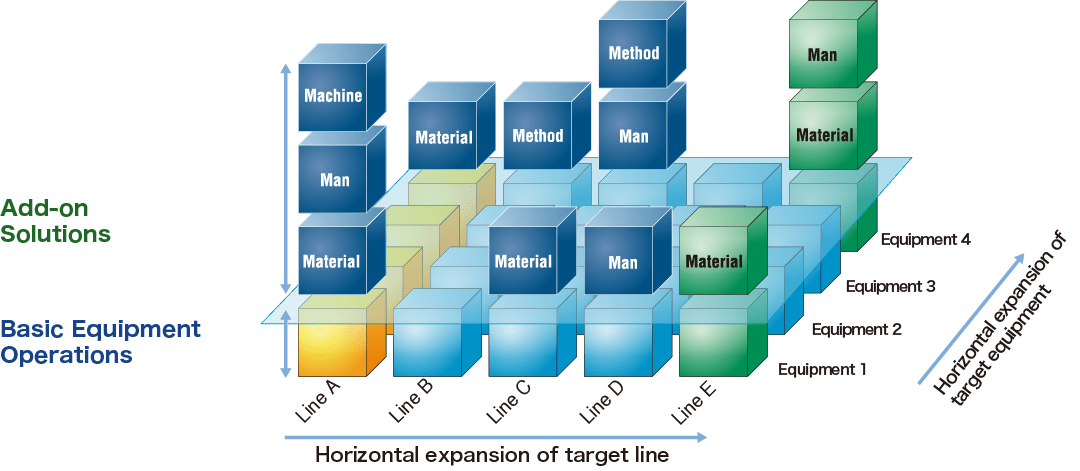
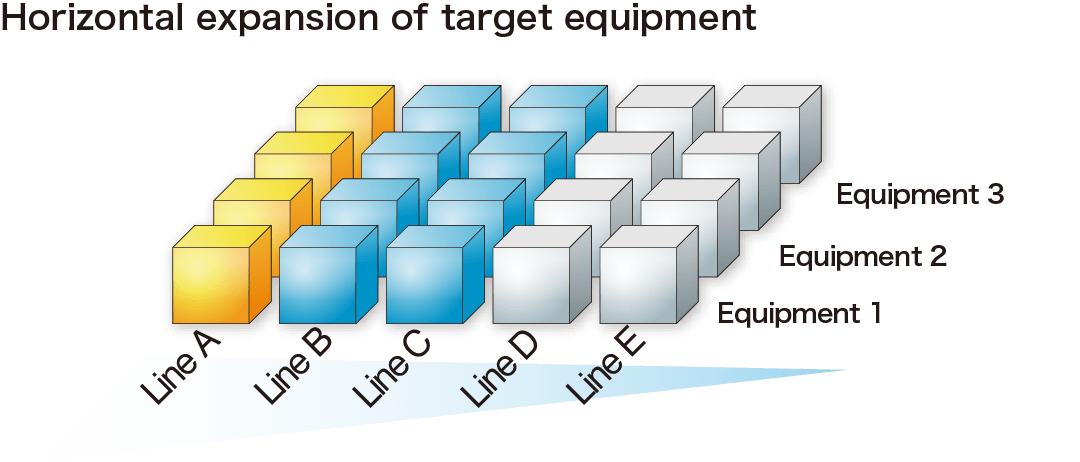
Develop a simple system that achieves horizontal results.
Simple example to
improve productivity
Develop a simple system that achieves results horizontally. By identifying similar equipment used in other production lines or facilities, greater improvements can be achieved with minimum investment.
Simple example to
improve productivity
Once basic implementation is complete, new requirements will arise. This can be at a different or same location, or additional areas for improvement can be identified. With the continued need to better visualize newly identified issues, it is important to keep in mind the previous steps: